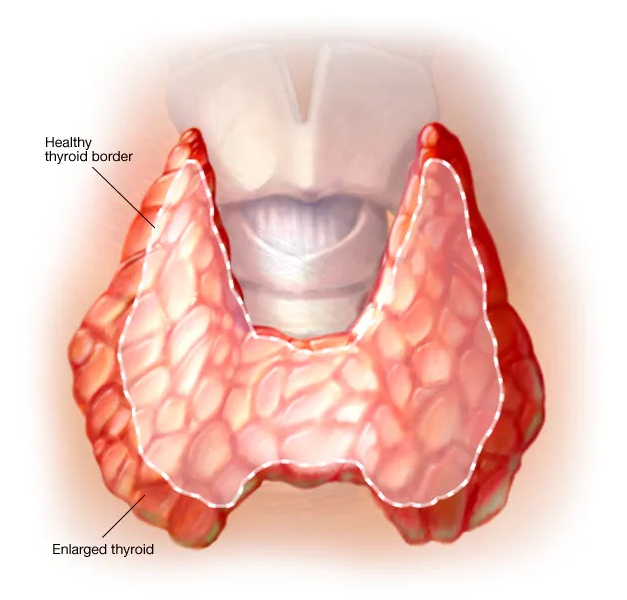
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder that causes the thyroid gland to become overactive, a condition known as hyperthyroidism. It’s one of the most common causes of hyperthyroidism in the United States. This disease occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid, causing it to produce more hormones than the body needs.
Graves’ Disease – Common symptoms
Common symptoms include weight loss, anxiety, hand tremors, heat sensitivity, fatigue, and a rapid or irregular heartbeat. One of the most recognizable signs is Graves’ ophthalmopathy—bulging eyes or eye discomfort. Though it can affect anyone, it’s more common in women under 40.
The exact cause of Graves’ disease isn’t known, but it’s believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Smoking, stress, and a family history of thyroid issues can increase the risk.
Graves’ disease is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical exams, blood tests, and imaging. Treatments include antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery to remove the thyroid gland.
see also: Daily Gut Routine with Natural Supplements
Early diagnosis and proper treatment are essential in managing symptoms and preventing complications. If left untreated, it can lead to serious issues like heart problems and brittle bones.